Acute prostatitis is the most common disease in men. It is most often diagnosed between the ages of 30 and 50 in nearly 60% of the male population.
In the acute form of prostatitis, an inflammatory process develops in the prostate gland. For the treatment of this stage of the disease, several groups of drugs are used, prostate massage, physiotherapy. The most important thing in treatment is to prevent the pathological transition to a chronic form.
Acute prostatitis in men and the reasons for its development
Acute prostatitis is the development of an inflammatory process in the prostate gland caused by the penetration of infection.
The disease is accompanied by swelling and pus in the prostate tissue.
This is the most common disease in men, which is accompanied by disorders of sexual function and fertility, disorders of psycho-emotional state, as well as social disorders.
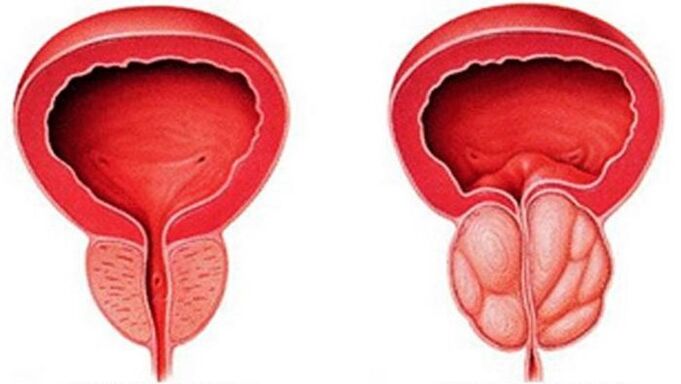
Acute forms of prostatitis
The development of acute prostatitis goes through 4 stages, which at the same time take the form of:
- cataract;
- follicle;
- parenchyma;
- purulent.
The disease begins with the development of catarrhal inflammation, causing changes in the mucosal layer and submucosa of the excretory tract of the glands. Edema of the duct wall causes stagnation of mucopurulent secretions in the prostate follicles. The inflammatory process begins to develop, causing focal suppuration of the lobules of the prostate gland. Acute follicular prostatitis is formed.
Multiple damage to the glandular lobules, structural changes in prostate tissue and the development of purulent -inflammatory processes in it lead to the next stage of the disease - parenchymal.
When many inflammatory foci merge into one large one, an abscess of the prostate gland forms. There is a possibility of opening it into the urethra, perineum, rectum or bladder cavity.
Causes of disease development
The following factors can cause acute prostatitis in men:
- Infectious processes in the genitourinary system. Infectious agents (gram-negative and gram-positive) can penetrate into prostate tissue: Escherichia coli, Proteus, staphylococci, streptococci. In many cases, the acute form of the disease can be caused by the causative agent of urogenital infections, such as: ureoplasmosis, chlamydia, mycoplasmosis, gonorrhea, candidiasis, etc.
- An infectious process that enters the urethra through the urethra. Microbes can enter prostate tissue through the excretory ducts of the prostate gland that open into the urethra. That is why any type of bladder inflammation is accompanied by acute prostatitis in men.
- An infectious process that enters the glands through the blood. The penetration of the infection into the prostate through the blood supply system is due to the extensively developed combined system of arteries and veins. Microbes in this case are carried through the circulatory system from the distant focus of purulent inflammation in diseases such as: tonsillitis, caries, sinusitis, bronchitis, cholecystitis and others.
- Sedentary lifestyle. As a result of low motor activity, stagnation of prostate gland juice is formed. This is facilitated by: long -term work at the computer, infrequent walking in the fresh air, smoking and drinking alcoholic beverages, infrequent sexual intercourse, refusal to active rest.
- Hypothermia. Long -term exposure to cold on the genitourinary system causes disruption in blood supply, which also leads to stagnation in the prostate, which gives rise to the onset of acute prostatitis.
- Injuries to the pelvic organs and prostate gland. When an injury is received, the release of secretions of the prostate gland is difficult, which leads to the development of inflammatory processes, which in turn leads to acute prostatitis.
- Medical procedures. Acute forms of prostatitis can develop as a result of chemotherapy or radiation therapy, as well as after medical examination through the urethra.
symptoms
The clinical picture in acute prostatitis is characterized by the presence of the following signs:
- Difficulty urinating
- feeling of incomplete emptying of the bladder;
- occurrence of frequent urge to urinate;
- itching and burning;
- dull aching pain in the head of the penis, radiating to the anus (when the pathology develops, the pain will become chronic);
- pain during defecation;
- increase in body temperature (from 37 to 40 degrees - depending on the stage of development of the disease);
- decreased sexual drive;
- erection problems;
- the content of pus and blood in the urine;
- deterioration in general well -being.
Treatment
Acute prostatitis, in contrast to chronic forms of the disease, responds well to therapy. Serious complications are extremely rare.
The most important task in drug treatment is to eliminate the patient of pain syndrome and pathological causative agents, to restore the normal process of urination.
Drugs used in the medical treatment of acute prostatitis:
- AntibioticsThe main group of drugs in the treatment of acute prostatitis. To choose an antibiotic, the doctor must accurately determine the causative agent of the disease. Often, a combination of antibiotics is prescribed, when one drug is taken in a course, after which it is replaced with another. This approach minimizes the development of re -inflammation and prevents the transition of the acute form of the disease to chronic. Antibiotics-fluoroquinolones, tetracyclines, penicillins have been successfully used.
- DiureticsDiuretics are prescribed to facilitate the process of urination and reduce stress. Diuretics promote regular and volume urine production. Herbal medicines and diuretics are used.
- Antipyretics. They are used to reduce body temperature, relieve pain in the joints and head.
- Antispasmodic. A drug that relaxes smooth muscles, relieves cramps. Also, medications in this group relieve pain and help relieve urination.
- Alpha blocker. Medicines that relieve cramps well, stimulate and facilitate the removal of urine from the patient.
After removing the main symptoms of the disease, prostate massage and physiotherapy procedures can be prescribed in addition.
After recovery, you must lead a healthy lifestyle.
Properly chosen treatment and compliance with all doctor’s prescriptions will eliminate acute prostatitis and prevent it from becoming chronic.